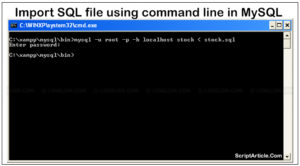
If your databases are located on same MySQL server.You don’t need two connections, you can access them both as unique user.
You also don’t need to select a DB. Just use the database-name as prefix when specifying the tables. That’s it.
<?php
mysql_connect("localhost","username","password") or die(mysql_error());
$query = "SELECT * FROM database1.tablename";
$result = mysql_query($query)or die(mysql_error());
var_dump($result);
$query2 = "SELECT * FROM database2.tablename";
$result2 = mysql_query($query2)or die(mysql_error());
var_dump($result2);
?>
Or if you want to select database, you can do
Please note there can only be one active DB at a time, it will work in this way:
<?php
$conn1 = mysql_connect("localhost","username","password") or die(mysql_error());
$conn2 = mysql_connect("localhost","username","password",true) or die(mysql_error());
mysql_select_db("database1",$conn1);
// tablename is a table of database1
$query = "SELECT * FROM tablename";
$result = mysql_query($query,$conn1);
var_dump($result);
mysql_select_db("database2",$conn2);
// tablename is a table of database2
$query2 = "SELECT * FROM tablename";
$result2 = mysql_query($query2,$conn2);
var_dump($result2);
?>
Although there’s no need for 2 connections; you can select both DB’s using the same connection.
You can make multiple calls to mysql_connect(), but if the parameters are the same you need to pass true for the ‘$new_link’ (fourth) parameter, otherwise the same connection is reused.
So then you have to do is
<?php
$db_conn1 = mysql_connect($hostname, $username, $password);
$db_conn2 = mysql_connect($hostname, $username, $password, true);
mysql_select_db('database1', $db_conn1);
mysql_select_db('database2', $db_conn2);
//Then to query database 1, do
mysql_query('select * from tablename', $db_conn1);
//and for database 2
mysql_query('select * from tablename', $db_conn2);
?>
It is used if MySQL server of database is different.